Unveiling the Profound Impact of Soil Erosion and Carbon Dynamics: A Comprehensive Guide for Conservationists, Farmers, and Policymakers

Soil, the foundation of life on Earth, is a dynamic system that faces numerous challenges, including erosion and carbon loss. These processes not only degrade soil health but also have far-reaching consequences for food security, climate change, and ecosystem stability. "Soil Erosion and Carbon Dynamics: Advances in Soil Science" is a comprehensive resource that delves into these critical issues, providing valuable insights and practical strategies for their mitigation.
 Soil Erosion and Carbon Dynamics (Advances in Soil Science) by Kenn Miller
Soil Erosion and Carbon Dynamics (Advances in Soil Science) by Kenn Miller4.2 out of 5
Language : English File size : 10446 KB Text-to-Speech : Enabled Screen Reader : Supported Enhanced typesetting : Enabled Print length : 623 pages
Soil Erosion: A Silent Threat
4.2 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 10446 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 623 pages |
Soil erosion refers to the wearing away of topsoil by natural processes like wind and water. It is a global problem that affects billions of hectares of land annually, leading to the loss of fertile soil, nutrients, and organic matter. This degradation poses a significant threat to agricultural productivity, as topsoil is essential for plant growth and crop yields.
Causes of Soil Erosion
Understanding the causes of soil erosion is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies. The primary factors contributing to this problem include:
* Excessive Tillage: Improper agricultural practices, such as over-tilling, can break down soil structure, making it more susceptible to erosion. * Deforestation: The removal of trees and other vegetation cover exposes soil to the elements, increasing the risk of erosion by wind and water. * Overgrazing: Excessive grazing by livestock can compact soil, reduce plant cover, and accelerate erosion. * Intense Rainfall: Heavy rainfall events can cause rapid runoff, carrying away topsoil and nutrients.
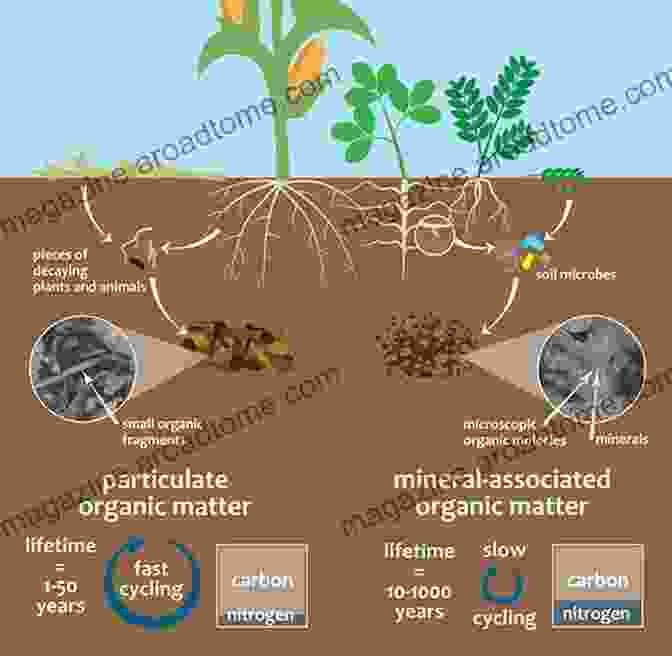
Carbon Dynamics: The Vital Soil-Atmosphere Exchange
Soil plays a critical role in the global carbon cycle, acting as a vast reservoir for organic carbon. Through the process of carbon sequestration, soil captures and stores carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating climate change. However, soil erosion and other disturbances can disrupt this delicate balance, releasing carbon back into the atmosphere.
Carbon Sequestration in Soil
Soil organic matter, a complex mixture of plant and animal residues, is the primary form of carbon stored in soil. Soil microbes break down organic matter, releasing carbon dioxide and nutrients for plant growth. However, under ideal conditions, a significant portion of organic carbon remains stored in soil, enhancing soil fertility and mitigating climate change.
Threats to Carbon Sequestration
Human activities and environmental changes can compromise soil's ability to sequester carbon:
* Land Use Change: Conversion of natural ecosystems to agriculture or urban areas reduces soil organic matter content. * Agricultural Practices: Intensive farming, excessive tillage, and burning can deplete soil carbon stocks. * Climate Change: Increased temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can accelerate organic matter decomposition, releasing carbon dioxide.

Unlocking Soil's Potential: Strategies for Mitigation and Management
Addressing soil erosion and carbon loss requires a multi-faceted approach that combines practical management techniques and policy initiatives. "Soil Erosion and Carbon Dynamics: Advances in Soil Science" provides comprehensive guidance on these strategies:
Soil Erosion Control Measures
* Terracing and Contour Farming: These practices create barriers that slow down runoff and reduce soil loss. * Cover Crops: Planting vegetation during fallow periods protects soil from wind and water erosion. * Mulching: Applying organic matter to the soil surface improves water retention and prevents erosion. * Conservation Tillage: Minimizing tillage practices preserves soil structure and reduces erosion risk.
Carbon Sequestration Enhancement
* Agroforestry: Integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural systems increases organic matter inputs and enhances carbon sequestration. * Conservation Agriculture: A holistic approach that combines soil erosion control and carbon sequestration practices. * Biochar Application: Adding biochar, a charcoal-like substance, to soil improves water retention and carbon storage capacity. * Improved Grazing Practices: Implementing rotational grazing and reducing livestock density minimizes soil compaction and promotes carbon sequestration.
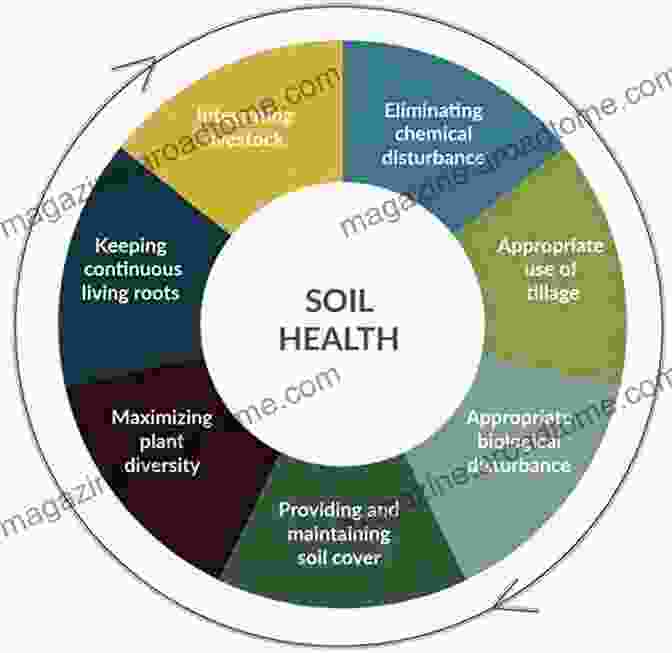
The Role of Policy and Collaboration
Tackling soil erosion and carbon dynamics requires a collaborative effort involving policymakers, scientists, farmers, and conservationists. "Soil Erosion and Carbon Dynamics: Advances in Soil Science" emphasizes the importance of:
* Incentive Programs: Financial assistance and incentives can encourage farmers to adopt soil conservation and carbon sequestration practices. * Research and Development: Continued research is crucial for developing innovative technologies and practices. * Education and Extension: Outreaching to farmers, landowners, and the public promotes awareness and encourages sustainable land use practices. * Global Partnerships: International cooperation is essential for sharing knowledge and addressing transboundary soil erosion and carbon management issues.
Soil Erosion and Carbon Dynamics: Advances in Soil Science" is an invaluable resource for anyone concerned about the future of our soils. This comprehensive guide provides a thorough understanding of the complex interactions between soil erosion, carbon dynamics, and their implications for food security, climate change, and ecosystem health. By embracing the strategies and recommendations presented in this book, we can collectively safeguard our soils, ensure sustainable agricultural practices, and contribute to a more resilient planet for generations to come.
4.2 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 10446 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 623 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Kav Partap Karamthasingh
Kav Partap Karamthasingh Karen Nelson Bell
Karen Nelson Bell Kendall Johnson
Kendall Johnson Karl Heinz Donnerhacke
Karl Heinz Donnerhacke Karen J Ragland
Karen J Ragland Rachelle Blondel
Rachelle Blondel Karen E Riggs
Karen E Riggs Suzanne Wagner
Suzanne Wagner Kelly Harland
Kelly Harland Kevin Kurtz
Kevin Kurtz Robert Langs
Robert Langs Kathleen Barnes
Kathleen Barnes Kathy Griffin
Kathy Griffin Karen Aken
Karen Aken Patti Polk
Patti Polk Tonya Duncan Ellis
Tonya Duncan Ellis Kevin Ambrose
Kevin Ambrose Kenneth Wong
Kenneth Wong Robert D Keppel
Robert D Keppel Kenneth M Heilman
Kenneth M Heilman
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Caleb LongUnveiling the Comprehensive Guide to Pennsylvania Employment Laws: Empowering...
Caleb LongUnveiling the Comprehensive Guide to Pennsylvania Employment Laws: Empowering...
 Troy SimmonsDelve into the Golden Age of Chicago Horse Racing through "Images of America"
Troy SimmonsDelve into the Golden Age of Chicago Horse Racing through "Images of America"
 Ivan TurgenevThe Geriatric Dental Hygienist and Geriatric Dentist Guide to Oral Care for...
Ivan TurgenevThe Geriatric Dental Hygienist and Geriatric Dentist Guide to Oral Care for... Jayden CoxFollow ·7.2k
Jayden CoxFollow ·7.2k Joseph ConradFollow ·12.5k
Joseph ConradFollow ·12.5k E.M. ForsterFollow ·10.6k
E.M. ForsterFollow ·10.6k Nathan ReedFollow ·13.3k
Nathan ReedFollow ·13.3k Elton HayesFollow ·14k
Elton HayesFollow ·14k Denzel HayesFollow ·11.7k
Denzel HayesFollow ·11.7k Paul ReedFollow ·9k
Paul ReedFollow ·9k Jordan BlairFollow ·13.4k
Jordan BlairFollow ·13.4k

 Francis Turner
Francis TurnerLearn to Make the Perfect Tapas Dishes Through the...
If you're looking to...

 Victor Turner
Victor TurnerUnlock the Secrets of Publishing Law: A Comprehensive...
Embark on a literary journey where the...

 Casey Bell
Casey BellHealing Crystals: Essential Crystals for Beginners
Unveiling the Mystical...

 Nick Turner
Nick TurnerOne Hundred Years of Fire Insurance: A History of...
Chapter 1: The...
4.2 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 10446 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 623 pages |