Insulin Resistance: Unmasking the Hidden Danger in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes

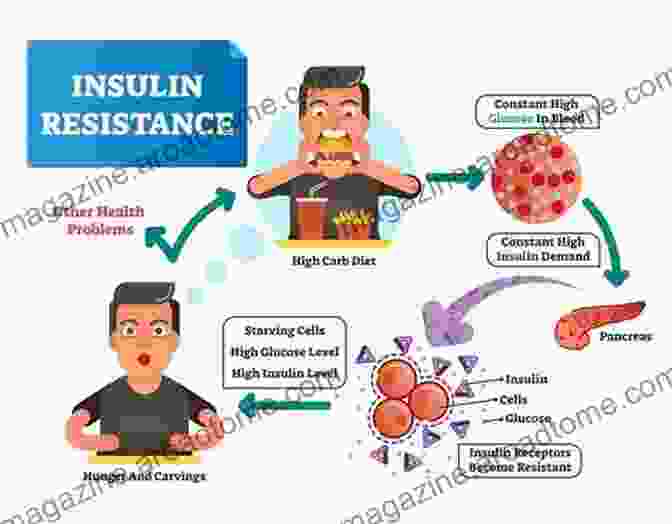
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide. While type 1 and type 2 diabetes have distinct causes, they share a common underlying factor: insulin resistance. This condition can lead to a cascade of health complications, making it crucial to understand its impact and management strategies.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 13377 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 122 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Insulin Resistance: The Basics
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps glucose (sugar) enter cells for energy production. In insulin resistance, the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
There are various factors that can contribute to insulin resistance, including:
* Obesity * Physical inactivity * Family history of diabetes * Certain medications * Metabolic disFree Downloads
Insulin Resistance and Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks the pancreas, destroying the insulin-producing cells. As a result, the body produces little or no insulin, leading to severe hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
While insulin resistance is not a direct cause of type 1 diabetes, it can play a role in the development of complications. Elevated blood glucose levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of eye disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by both insulin resistance and insufficient insulin production. When cells become resistant to insulin, the pancreas attempts to compensate by producing more insulin. However, over time, the pancreas may become unable to keep up with the demand, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
Insulin resistance is the primary driving force behind the development of type 2 diabetes. Studies have shown that people with insulin resistance are at significantly higher risk of developing the condition.
Consequences of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance can have wide-ranging consequences for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes:
* Elevated Blood Glucose: Insulin resistance leads to higher blood sugar levels, which can damage blood vessels and organs over time. * Cardiovascular Disease: Insulin resistance is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications. * Kidney Disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney disease and potentially kidney failure. * Neuropathy: Elevated blood glucose can damage the nerves, causing pain, numbness, and tingling. * Eye Disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy and potential vision loss.
Managing Insulin Resistance
Managing insulin resistance is crucial for preventing or managing diabetes and its complications. Key strategies include:
* Lifestyle Changes: Losing weight, exercising regularly, and adopting a healthy diet can improve insulin sensitivity. * Medications: Medications such as metformin and thiazolidinediones can increase insulin sensitivity and lower blood glucose levels. * Insulin Therapy: For people with type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy may be necessary to control blood glucose levels.
Ignite Your Health Journey
If you have been diagnosed with diabetes or are at risk for developing the condition, understanding the role of insulin resistance is essential. By following the strategies outlined in this book, you can take control of your insulin resistance, improve your blood glucose control, and reduce your risk of serious complications.
Free Download Your Copy Today
Embrace the power of knowledge and Free Download your copy of "How Insulin Resistance In Type Diabetes And Type Diabetes Triggers Your Risk" today. This comprehensive guide will empower you with the essential information and tools you need to manage insulin resistance, optimize your health, and live a fulfilling and disease-free life.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 13377 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 122 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Stephen Ecker
Stephen Ecker Rob Bell
Rob Bell Keith L Gisser
Keith L Gisser Kathleen Deyer Bolduc
Kathleen Deyer Bolduc Kathleen Barnes
Kathleen Barnes Kim Harrison
Kim Harrison Kateri Ewing
Kateri Ewing Kathrina Simonen
Kathrina Simonen Jonathan Gleadle
Jonathan Gleadle Michelle Strong
Michelle Strong Terry M Boardman
Terry M Boardman Neeraj Kumar
Neeraj Kumar Vicki Karaminas
Vicki Karaminas Kenneth Barker
Kenneth Barker Thea Dennis
Thea Dennis Stefan Al
Stefan Al Ken Allsen
Ken Allsen Kenneth W Noe
Kenneth W Noe Stuart J Schnitt
Stuart J Schnitt Kade Young
Kade Young
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Colt SimmonsAtlanta: The Big Peach: A Captivating Social Studies Reader for Curious Minds
Colt SimmonsAtlanta: The Big Peach: A Captivating Social Studies Reader for Curious Minds
 Dakota PowellUnlock the Vibrant Secrets of French Color Design: A Journey Through Dover...
Dakota PowellUnlock the Vibrant Secrets of French Color Design: A Journey Through Dover... Gage HayesFollow ·4.4k
Gage HayesFollow ·4.4k Jason HayesFollow ·7.1k
Jason HayesFollow ·7.1k Will WardFollow ·16.4k
Will WardFollow ·16.4k Randy HayesFollow ·8.8k
Randy HayesFollow ·8.8k John Dos PassosFollow ·5.9k
John Dos PassosFollow ·5.9k Oscar BellFollow ·11.9k
Oscar BellFollow ·11.9k W.B. YeatsFollow ·6.3k
W.B. YeatsFollow ·6.3k Adrian WardFollow ·17.7k
Adrian WardFollow ·17.7k

 Francis Turner
Francis TurnerLearn to Make the Perfect Tapas Dishes Through the...
If you're looking to...

 Victor Turner
Victor TurnerUnlock the Secrets of Publishing Law: A Comprehensive...
Embark on a literary journey where the...

 Casey Bell
Casey BellHealing Crystals: Essential Crystals for Beginners
Unveiling the Mystical...

 Nick Turner
Nick TurnerOne Hundred Years of Fire Insurance: A History of...
Chapter 1: The...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 13377 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 122 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |